Find what is my DNS server?
Tips and Tricks to easily find itFind what is my DNS server
Are you experiencing slow internet speeds, frequent connectivity issues, or trouble accessing websites? Your DNS server may be the culprit.
But don’t worry, finding your DNS server doesn’t have to be a daunting task. In fact, with just a few tips and tricks, you can locate your DNS server in seconds and take control of your internet connection.
Whether you’re a tech-savvy user or a beginner, this guide will provide you with everything you need to know to find your DNS server and troubleshoot any issues that may arise. So, buckle up and get ready to discover the power of your DNS server!
Also read : Unbiased Porkbun Review: Is It a Good Domain Registrar for Your Website?
What is a DNS server?
A Domain Name System (DNS) server translates domain names to IP addresses. It is what makes your computer able to find the website you are looking for, what gives meaning to the domain name.
How does it work?
When you search for google.com into your web browser, the DNS server translates that into an IP address (i.e. Google’s IP address) and sends you to the site. Your computer stores the DNS server’s IP address (in this case Google’s IP address) in a local file.
So, how does the DNS system ensure that there is always an available server to handle your requests? It does so by employing a network of primary and secondary DNS servers.
Primary and secondary DNS servers
There is not only one server. Take the Google DNS for example, at the address 8.8.8.8.
If all the requests go to this server, the server will go down. To avoid this problem, the requests are routed to plenty of other DNS servers containing the same data.
Primary DNS server
A primary DNS server is the first server allowed to transform a domain name into an IP address.
It contains a file called the controlling zone file where all the authoritative data about the domain are written. It is the trusted source of all the domain information (IP address, administror contact, …).
Secondary DNS server
Secondary servers can do the same as the primary servers in order to distribute the load of requests.
The secondary server also contains a controlling zone file but only in a read only mode. This ensures to always have the same data between the primary and the secondary servers.
Changes to DNS records can only be done on the primary server. The information is updated in the secondary servers by a process called zone transfer.
It is recommended to have seondary DNS in order to ensure that all requests can be treated correctly
Why is the DNS server really important for your browsing safety?
The DNS server is what allows you to switch from a domain name to an IP address, which allows your computer to communicate with the desired website.
Imagine you want to check your banck account on the bank website. You write the bank domain in your web browser and wait to reach the page. The DNS server ensures you go to the real one and not a fake one.
If you use a malicious DNS server, for example run by a hacker, you could be redirected to a malicious site.
So if this is the case or if you want to change it, you need to understand the DNS settings.
DNS settings on your computer
Usually the DNS settings are made by your ISP (Internet Service Provider), but you can act on them if necessary. Here is how to do it.
How do I find my dns server?
There are different ways to find your DNS server, depending on the operating system you are using. Here are the most common methods:
On Windows:
- Open the Command Prompt (Press the “Windows key” + “R” and type “cmd” in the “Run” dialog box).
- Type “ipconfig /all” and press “Enter”.
- Look for the “DNS Servers” line to see the IP address of your DNS server(s).
On Mac:
- Click on the Apple icon in the top-left corner of your screen and select “System Preferences”.
- Click on “Network” and select your active network connection (Wi-Fi or Ethernet).
- Click on “Advanced” and select the “DNS” tab.
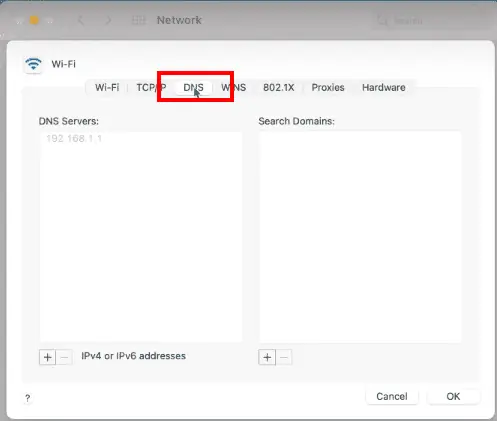
- Look for the IP address of your DNS server(s) in the “DNS Servers” section.
On Linux:
- Open the terminal.
- Type “cat /etc/resolv.conf” and press “Enter”.
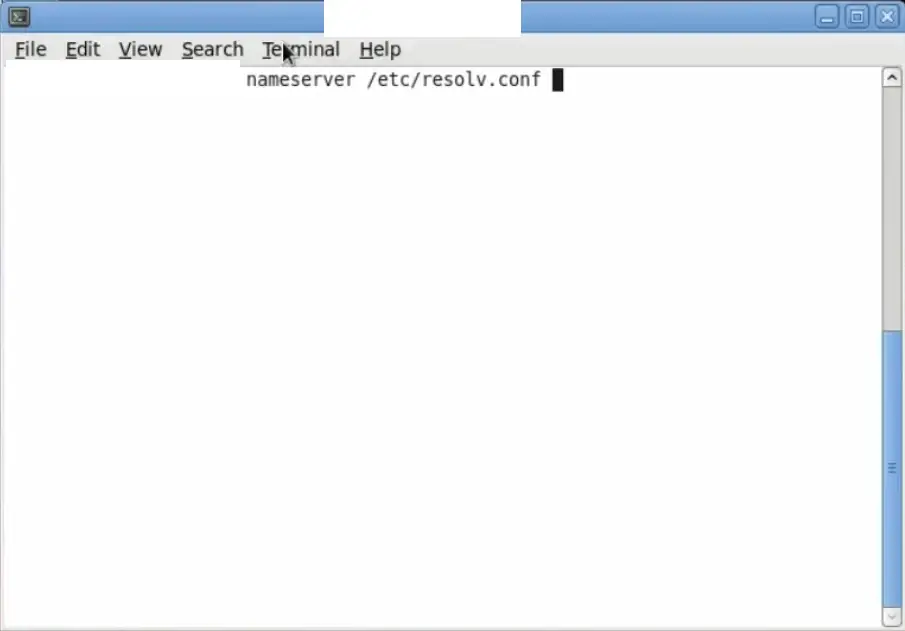
- Look for the IP address of your DNS server(s) in the “nameserver” lines.
If you are using a router to connect to the internet, you can also check the DNS server settings in your router’s configuration page. Keep in mind that you may have multiple DNS servers, and the order in which they are listed may affect your internet connection speed and reliability.
How do I change my DNS server?
To change your DNS server, you will need to access your network settings and update the DNS server address. Here are the steps to change your DNS server on some common operating systems:
To change and configure your DNS server On Windows:
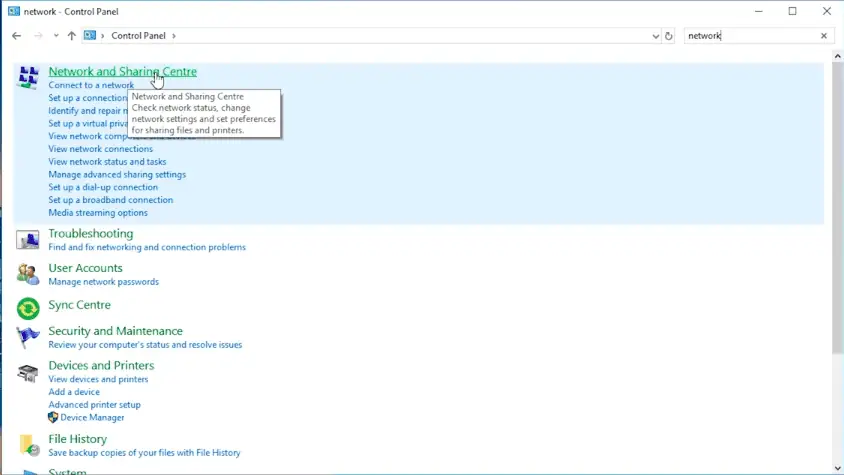
- Open the Control Panel and click on “Network and Sharing Center”.
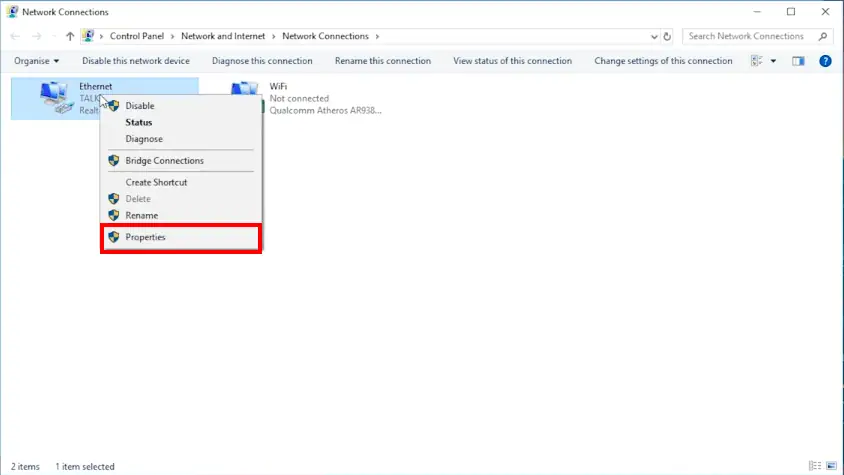
- Click on your active network connection and select “Properties”.
- Select “Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/ IPv 4)” and click on “Properties”.
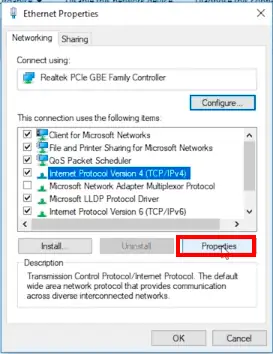
- Select the “Use the following DNS server addresses” option and type the IP address of your preferred DNS server(s).
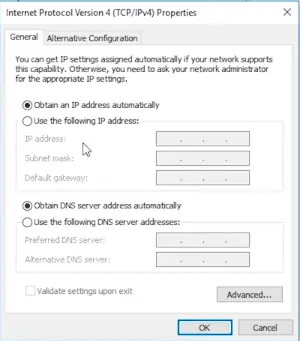
- Click “OK” to save the changes.
To change and configure your DNS on Mac:
- Click on the Apple icon in the top-left corner of your screen and select “System Preferences”.

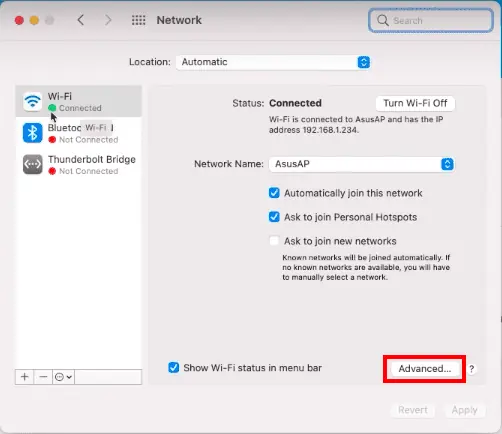
- Click on “Network” and select your active network connection (Wi-Fi or Ethernet).

- Click on “Advanced” and select the “DNS” tab.
- Click on the “+” button and write the IP address of your preferred DNS server(s).
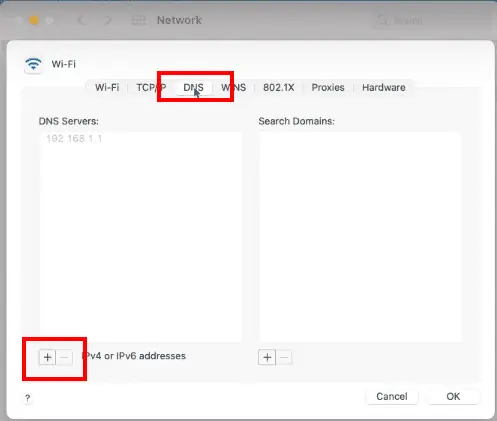
- Click “OK” to save the changes.
To change & configure on Linux:
- Open the terminal.
- Type “sudo nano /etc/resolv.conf” and press “Enter”.
- Replace the existing nameserver addresses with the IP address of your preferred DNS server(s).
- Press “Ctrl+O” to save the changes and “Ctrl+X” to exit the editor.
After changing your server, you may need to flush your caches to ensure that the new settings take effect. This can be done by typing “ipconfig /flushdns” (on Windows) or “sudo systemd-resolve –flush-caches” (on Linux) in the terminal.
What’s the DNS cache exactly?
The cache refers to the temporary storage of DNS records on your device or network. These records contain information such as the IP address associated with a specific domain name.
When you access a site, your device first checks its local file to see if it already has the IP address for that website. If it does, it can quickly load the page without having to look up the IP address again. This can speed up your internet browsing experience.
However, if the IP address is outdated or incorrect, you may experience issues accessing the page. In this case, you may need to clear your DNS cache to force your device to perform a fresh Domain Name System lookup.
How to flush DNS cache?
But, if your cache DNS has been poisoned, i.e. a domain is not assigned to the real website, you can flush the DNS.
On Windows
- Open the Command Prompt as an administrator (Press the “Windows key” + “X” and select “Command Prompt (Admin)”).
- Type “ipconfig /flushdns” and press “Enter”.
- You should see a message saying “Successfully flushed the DNS Resolver Cache”.
On Mac
- Open the terminal.
- Type “sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder” and press “Enter”.
On Linux
- Open the terminal.
- Type “sudo systemd-resolve –flush-caches” and press “Enter”.
After flushing it, you may need to wait a few seconds or minutes for the cache to fully clear. Once the everything is cleared, your device will need to perform fresh DNS lookups for all the websites you visit, which may initially slow down your browsing experience.
However, this should only be temporary, and your browsing experience should improve once the cache is rebuilt with fresh DNS records.
Find your DNS: the important points to keep in mind
In conclusion, understanding DNS servers is essential for a safe and efficient browsing experience.
Knowing how to find and change your DNS server settings on your device or network can help improve internet connection reliability and speed, and prevent malicious websites from harming your device or stealing your information.
As you have learned, DNS plays a crucial role in the browsing experience. Clearing your DNS caches can be necessary in some situations. Remember, updating your DNS settings can be a simple solution to internet connection problems, and help ensure you always reach the real website when surfing the internet.